Sindrome di Ehlers-Danlos tipo 1 OMIM 13000 tipo 2 OMIM 130010
Sindrome di Ehlers-Danlos tipo 1 OMIM 130000 tipo 2 OMIM 130010
Col termine Sindrome di Ehlers-Danlos sono comprese un complesso eterogeneo di malattie ereditarie del tessuto connettivo distinte in sei tipi differenti in rapporto ai geni coinvolti ed alle caratteristiche cliniche.
Il tipo classico, che comprende i tipi 1 e 2, è caratterizzato da tre manifestazioni principali: iperlassità articolare, iperestensibilià della cute, formazione di cicatrici anomale sulla pelle.
La genetica è legata mutazioni di vari geni; il 50% delle forme classiche è dovuta a mutazioni dei geni COL5A1 o COL5A2 che codificano per il collagene di tipo V. La trasmissione è autosomica dominante e la mutazione può essere ereditata dai genitori oppure comparire de novo; vi sono anche forme a trasmissione autosomica recessiva e forme recessive legate all'X.
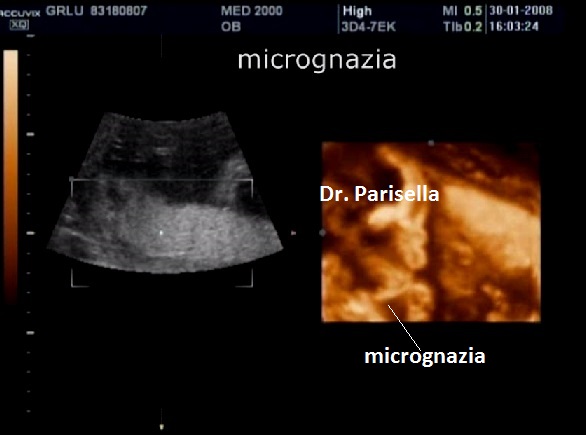
La diagnosi prenatale può essere sospettata se presenti alcune anomalie muscolo-scheletriche: ginocchio recurvato congenito, micrognazia, dislocazione del radio, piede torto, spondilolisi, spondilolistesi.
Bibliografia
Tipo 1
Barabas, A. P. Heterogeneity of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome:
description of three clinical types and a hypothesis to explain the basic
defect(s). Brit. Med. J. 2: 612-613, 1967.
Beighton, P. The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes.In: Beighton, P.
(ed.) : McKusick's Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue. 5th ed. St. Louis:
Mosby 1993. Pp. 189-251.
Beighton, P., De Paepe, A., Steinmann, B., Tsipouras, P.,
Wenstrup, R. J. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997.
Am. J. Med. Genet. 77: 31-37, 1998.
Borck, G., Beighton, P., Wilhelm, C., Kohlhase, J., Kubisch,
C. Arterial rupture in classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with COL5A1 mutation. Am.
J. Med. Genet. 152A: 2090-2093, 2010.
Burrows, N. P., Nicholls, A. C., Yates, J. R. W., Gatward,
G., Sarathachandra, P., Richards, A., Pope, F. M. The gene encoding collagen
alpha-1(V) (COL5A1) is linked to mixed Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I/II. J.
Invest. Derm. 106: 1273-1276, 1996.
Castori, M., Camerota, F., Celletti, C., Grammatico, P.,
Padua, L. Quality of life in the classic and hypermobility types of Elhers
(sic)-Danlos syndrome. Neurology 67: 145-146, 2010.
Cuckow, P. M., Blackhall, R. J. S., Mouriquand, P. D. E.
Huge bladder diverticula associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J. Roy. Soc.
Med. 87: 290-291, 1994.
De Felice, C., Toti, P., Di Maggio, G., Parrini, S.,
Bagnoli, F. Absence of the inferior labial and lingual frenula in Ehlers-Danlos
syndrome. Lancet 357: 1500-1502, 2001.
Deodhar, A. A., Woolf, A. D. Ehlers Danlos syndrome and
osteoporosis. (Letter) Ann. Rheum. Dis. 53: 841-842, 1994.
Hines, C., Jr., Davis, W. D. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with
megaduodenum and malabsorption syndrome secondary to bacterial overgrowth: a
report of the first case. Am. J. Med. 54: 539-543, 1972.
Malfait, F., Coucke, P., Symoens, S., Loeys, B., Nuytinck,
L., De Paepe, A. The molecular basis of classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a
comprehensive study of biochemical and molecular findings in 48 unrelated
patients. Hum. Mutat. 25: 28-37, 2005.
Nuytinck, L., Freund, M., Lagae, L., Pierard, G. E.,
Hermanns-Le, T., De Paepe, A. Classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by a
mutation in type I collagen. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66: 1398-1402, 2000.
Sestak, Z. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and cutis laxa: an account
of families in the Oxford area. Ann. Hum. Genet. 25: 313-321, 1962.
Sokolov, B. P., Prytkov, A. N., Tromp, G., Knowlton, R. G.,
Prockop, D. J. Exclusion of COL1A1, COL1A2, and COL3A1 genes as candidate genes
for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I in one large family. Hum. Genet. 88: 125-129,
1991.
Steinmann, B., Royce, P. M., Superti-Furga, A. The
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.In: Royce, P. M.; Steinmann, B. (eds.) : Connective
Tissue and its Heritable Disorders: Molecular, Genetic, and Medical Aspects.
2nd ed. New York: Wiley Liss 2002. Pp. 431-524.
Symoens, S., Syx, D., Malfait, F., Callewaert, B., De
Backer, J., Vanakker, O., Coucke, P., De Paepe, A. Comprehensive molecular
analysis demonstrates type V collagen mutations in over 90% of patients with
classic EDS and allows to refine diagnostic criteria. Hum. Mutat. 33:
1485-1493, 2012.
Voermans, N. C., van Alfen, N., Pillen, S., Lammens, M.,
Schalkwijk, J., Zwarts, M. J., van Rooij, I. A., Hamel, B. C. J., van Engelen,
B. G. Neuromuscular involvement in various types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Ann. Neurol. 65: 687-697, 2009.
Vogel, A., Holbrook, K. A., Steinmann, B., Gitzelmann, R.,
Byers, P. H. Abnormal collagen fibril structure in the gravis form (type I) of
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Lab. Invest. 40: 201-206, 1979.
Wenstrup, R. J., Langland, G. T., Willing, M. C., D'Souza,
V. N., Cole, W. G. A splice-junction mutation in the region of COL5A1 that
codes for the carboxyl propeptide of pro-alpha-1(V) chains results in the
gravis form of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (type I). Hum. Molec. Genet. 5:
1733-1736, 1996.
Wenstrup, R. J., Meyer, R. A., Lyle, J. S., Hoechstetter,
L., Rose, P. S., Levy, H. P., Francomano, C. A. Prevalence of aortic root
dilation in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Genet. Med. 4: 112-117, 2002.
Zalis, E. G., Roberts, D. C. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with a
hypoplastic kidney, bladder diverticulum, and diaphragmatic hernia. Arch. Derm.
96: 540-544, 1967. [PubMed: 4964142, related citations] [Full Text: HighWire
Press]
Tipo 2
Beighton, P. The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes.In: Beighton, P.
(ed.) : McKusick's Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue. 5th ed. St. Louis:
Mosby 1993. Pp. 189-251.
Beighton, P. The Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. London: William
Heinemann (pub.) 1970.
Beighton, P., De Paepe, A., Steinmann, B., Tsipouras, P.,
Wenstrup, R. J. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997.
Am. J. Med. Genet. 77: 31-37, 1998.
Burrows, N. P., Nicholls, A. C., Yates, J. R. W., Gatward,
G., Sarathachandra, P., Richards, A., Pope, F. M. The gene encoding collagen
alpha-1(V) (COL5A1) is linked to mixed Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type I/II. J.
Invest. Derm. 106: 1273-1276, 1996.
De Felice, C., Toti, P., Di Maggio, G., Parrini, S.,
Bagnoli, F. Absence of the inferior labial and lingual frenula in Ehlers-Danlos
syndrome. Lancet 357: 1500-1502, 2001.
De Paepe, A., Nuytinck, L., Hausser, I., Anton-Lamprecht,
I., Naeyaert, J.-M. Mutations in the COL5A1 gene are causal in the
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes I and II. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 60: 547-554, 1997.
Loughlin, J., Irven, C., Hardwick, L. J., Butcher, S.,
Walsh, S., Wordsworth, P., Sykes, B. Linkage of the gene that encodes the
alpha-1 chain of type V collagen (COL5A1) to type II Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
(EDS II). Hum. Molec. Genet. 4: 1649-1651, 1995.
Richards, A. J., Martin, S., Nicholls, A. C., Harrison, J.
B., Pope, F. M., Burrows, N. P. A single base mutation in COL5A2 causes
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type II. J. Med. Genet. 35: 846-848, 1998.
Scarbrough, P. R., Daw, J., Carroll, A. J., Finley, S. C. An
unbalanced (6q;13q) translocation in a male with clinical features of
Ehlers-Danlos type II syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 21: 226-228, 1984.
Steinmann, B., Royce, P. M., Superti-Furga, A. The
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.In: Royce, P. M.; Steinmann, B. (eds.) : Connective
Tissue and its Heritable Disorde4rs: Molecular, Genetic, and Medical Aspects.
2nd ed. New York: Wiley Liss 2002. Pp. 431-524.
Symoens, S., Syx, D., Malfait, F., Callewaert, B., De
Backer, J., Vanakker, O., Coucke, P., De Paepe, A. Comprehensive molecular
analysis demonstrates type V collagen mutations in over 90% of patients with
classic EDS and allows to refine diagnostic criteria. Hum. Mutat. 33:
1485-1493, 2012.
Wenstrup, R. J., Meyer, R. A., Lyle, J. S., Hoechstetter,
L., Rose, P. S., Levy, H. P., Francomano, C. A. Prevalence of aortic root
dilation in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Genet. Med. 4: 112-117, 2002.
Aggiornamenti
- Patologie Genetiche dello Scheletro
Sono elencate tutte le 436 Displasie Scheletriche con la... - Consigli per l'utilizzo del software diagnosi in Diagnosi...
Consigli per l'utilizzo del software diagnosi in Diagnosi... - TERMINI DI USO DEL PORTALE WEB med2000eco e Software...
TERMINI DI USO DEL PORTALE WEB med2000eco e Software...